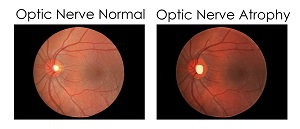
What is Optic Nerve Atrophy?
The optic nerve is a set of nerve fibers that carry information of what the eye perceives to the brain for conversion into images. Optic nerve atrophy is a condition in which a few or most of the optic nerve fibers are lost causing disruption of information sent to the brain. It is characterized by blurred vision, decreased perception of brightness, abnormal side and color vision.
Causes of Optic Nerve Atrophy
Optic nerve atrophy may be caused due to:
- Underdevelopment or inflammation of the optic nerve
- Increased pressure in the eye (glaucoma),
- Poisoning
- Vitamin deficiencies or tumors.
Optic nerve atrophy can be diagnosed by assessing your color vision, side vision and pupil’s reaction to light. Your doctor uses an ophthalmoscope to determine the loss of optic nerve fibers. MRI scans can also be used to confirm the diagnosis. Optic nerve atrophy cannot be treated as the nerve fibers that are lost cannot be healed. However, if the underlying cause for the condition is determined early and treated, further damage to the optic nerves can be controlled.
Related Topics
- Cataract
- Glaucoma
- Eyelid Disorders
- Dry Eyes
- Blepharitis
- Chalazion
- Tear Duct Obstruction
- Refractive Errors
- Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
- Pterygium
- Hyphema
- Herpetic Eye Disease
- Acute/ Chronic/Recurrent Iridocyclitis
- Chemical Burn
- Conjunctival & Corneal tear
- Repair of Conjunctival and Corneal tear
- Corneal Opacity
- Corneal Ulcer
- Ocular/Orbital Trauma
- Treatment of Ocular/Orbital trauma
- Eyelid Cyst
- Optic Nerve Atrophy
- Optic Neuropathy
- Pars Planitis/Intermediate Uveitis
- Posterior Uveitis
- Diseases of Cornea
- Temporal Arteritis
- Traumatic Iritis
- Ocular/Orbital Tumors
- Pediatric Eye Problems

